Imitation Learning for Robot Arm (Position / Force Control)
Bi-AQUA
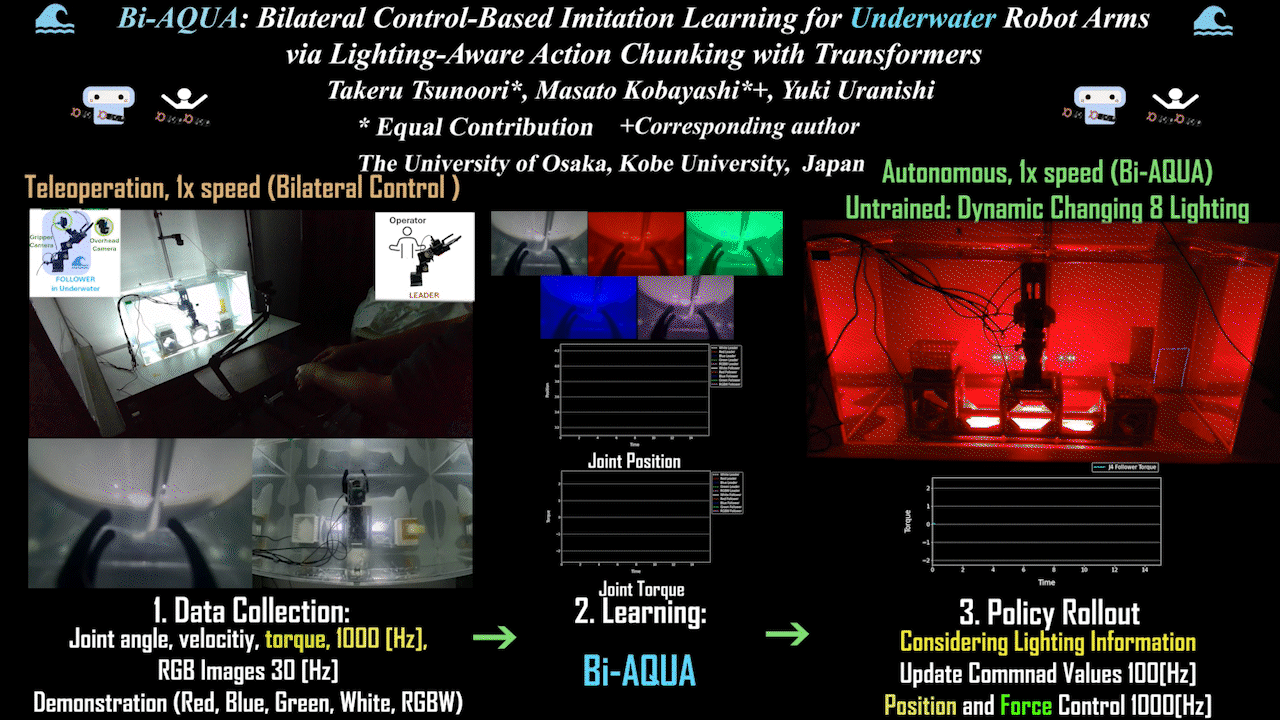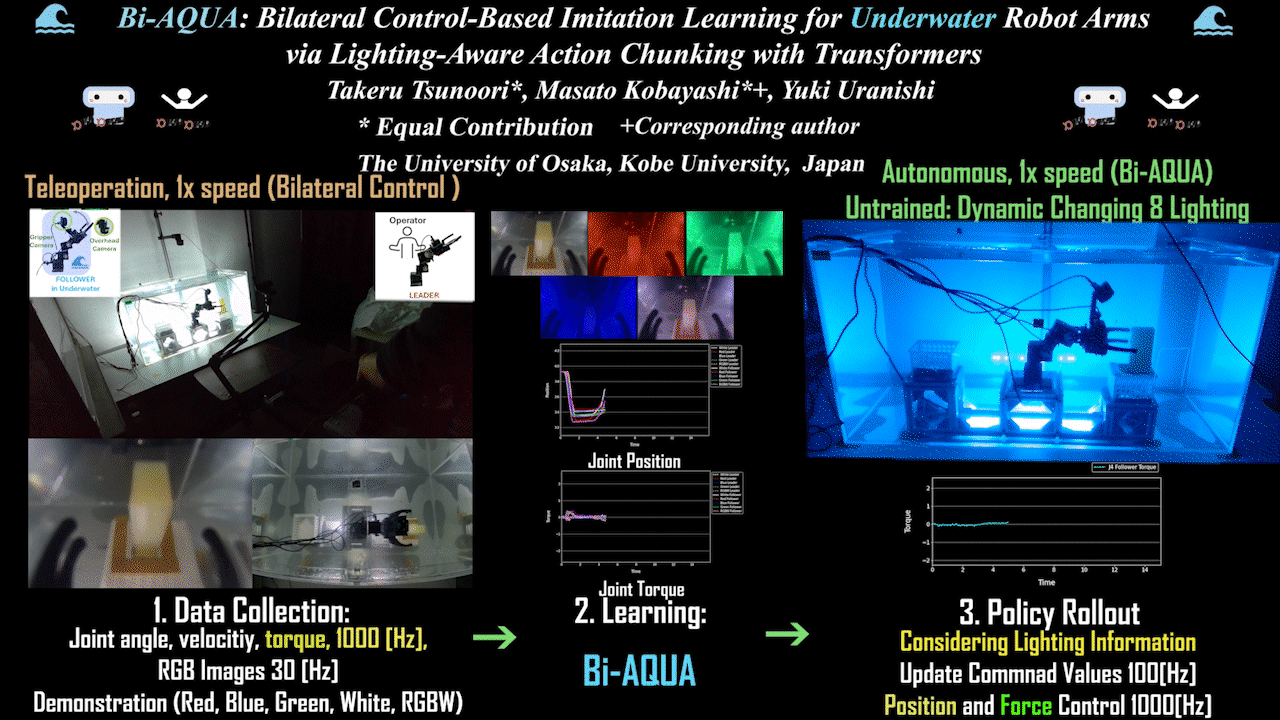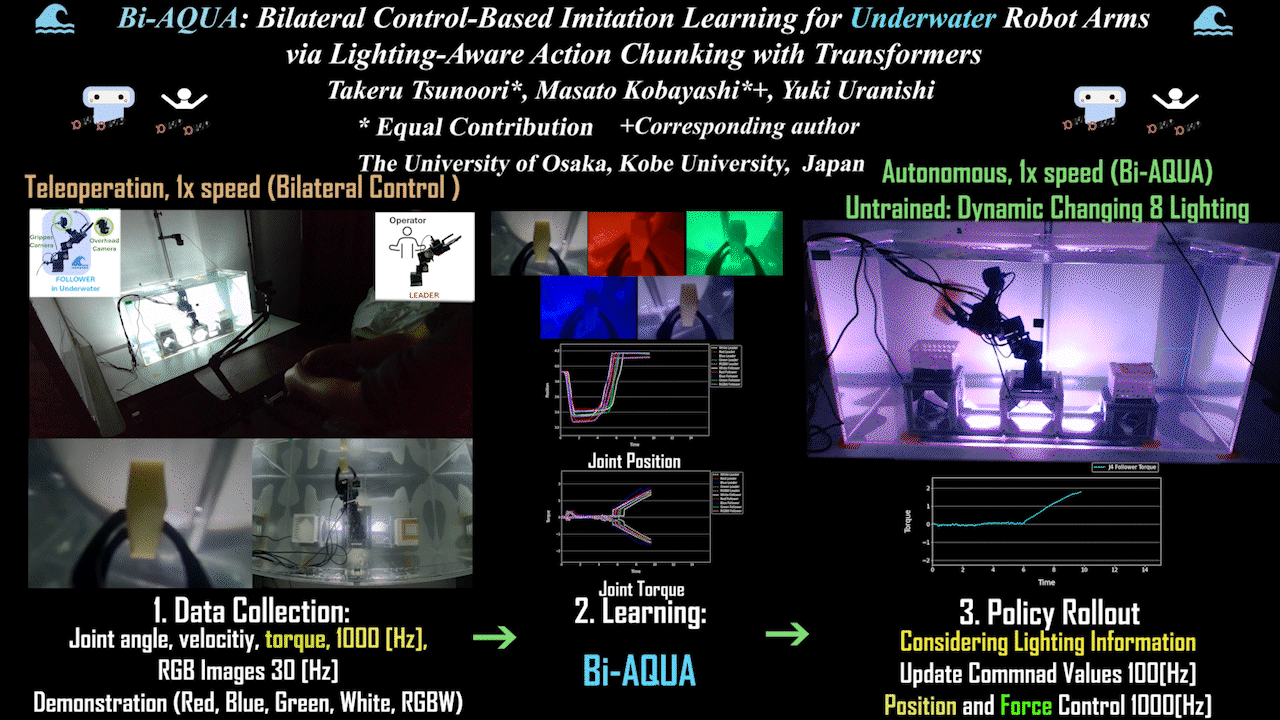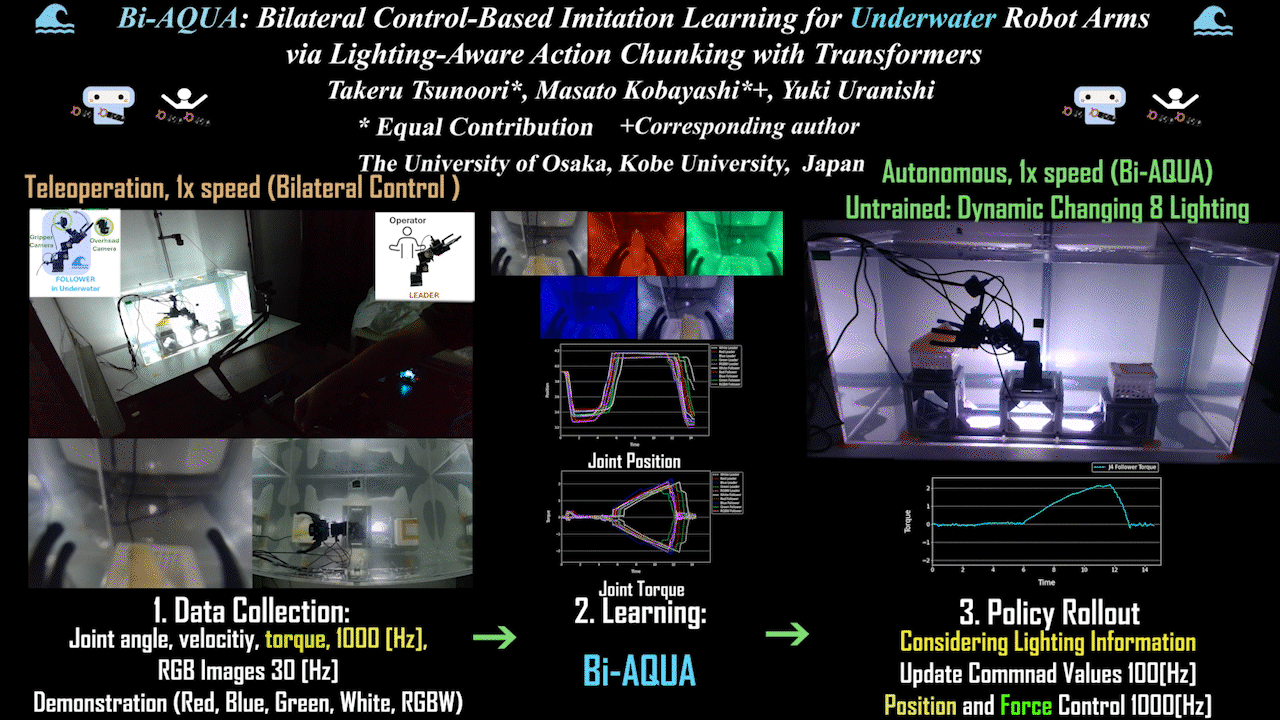
Bi-AQUA: Bilateral Control-Based Imitation Learning for Underwater Robot Arms via Lighting-Aware Action Chunking with Transformers
The world’s first bilateral control-based imitation learning for underwater environments realized in the real world. Robot learning model based on underwater/above-water images, lighting, position, and force information, with autonomous operation via position and force control.
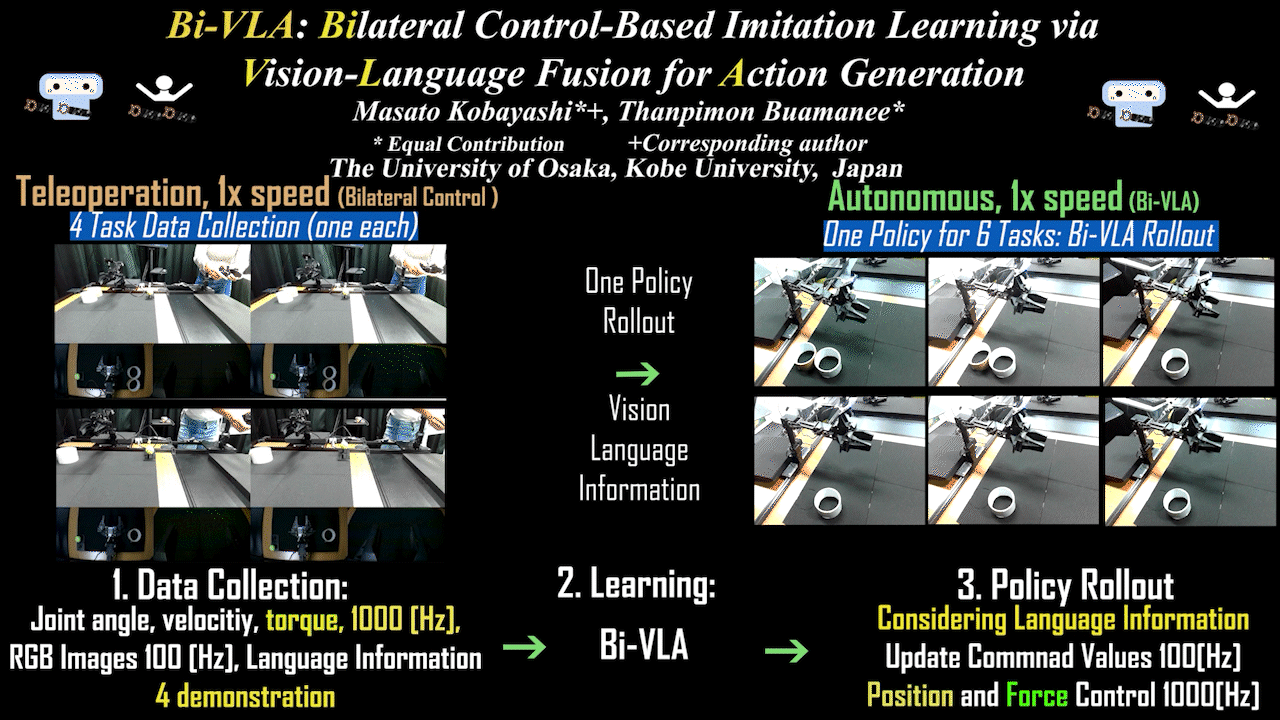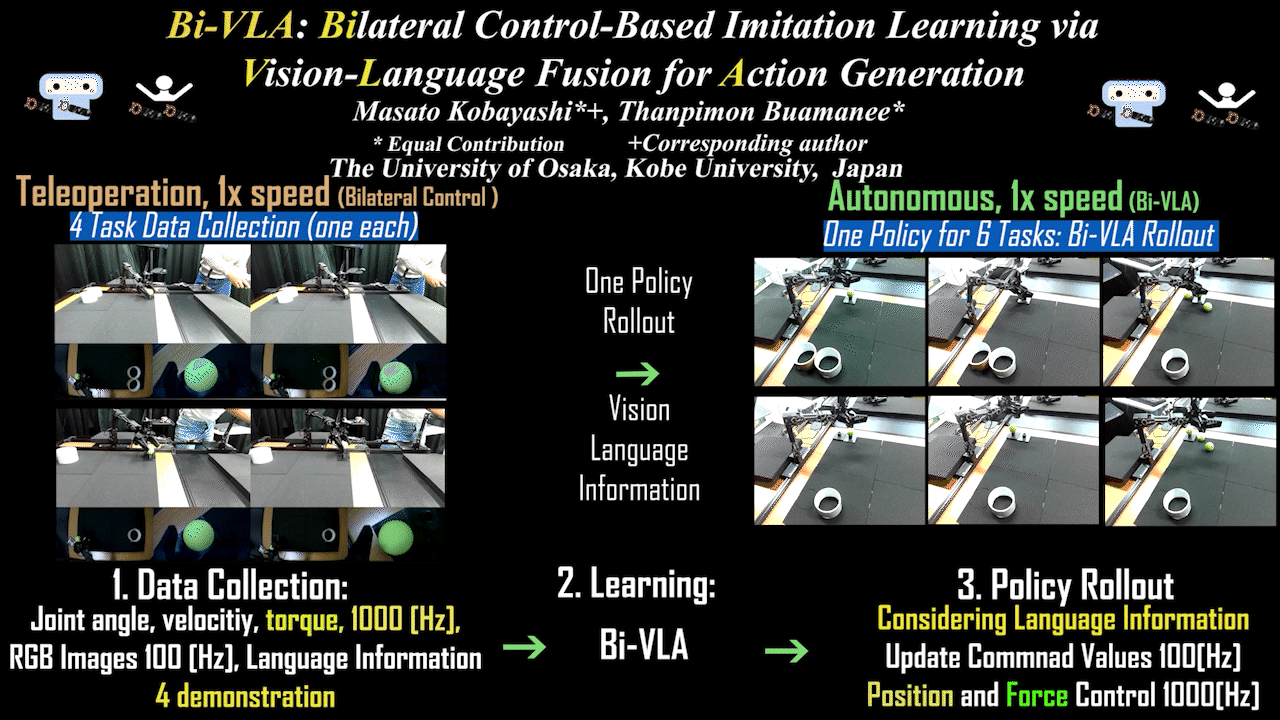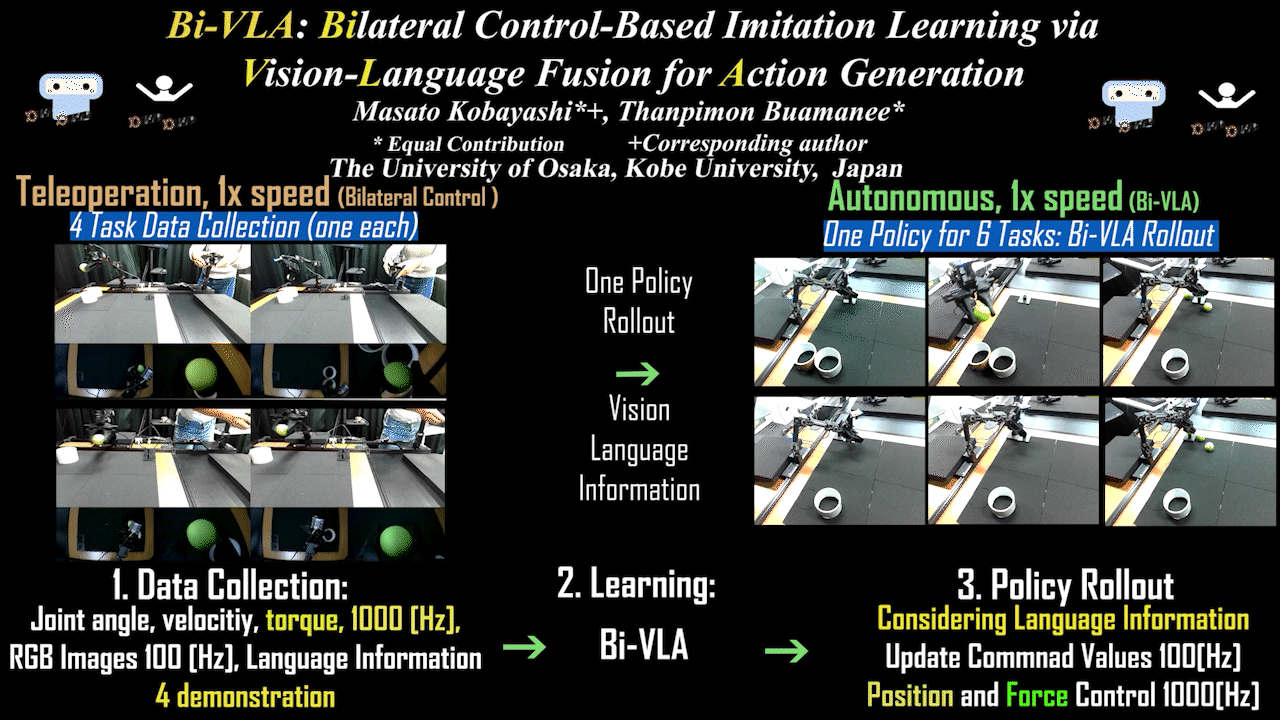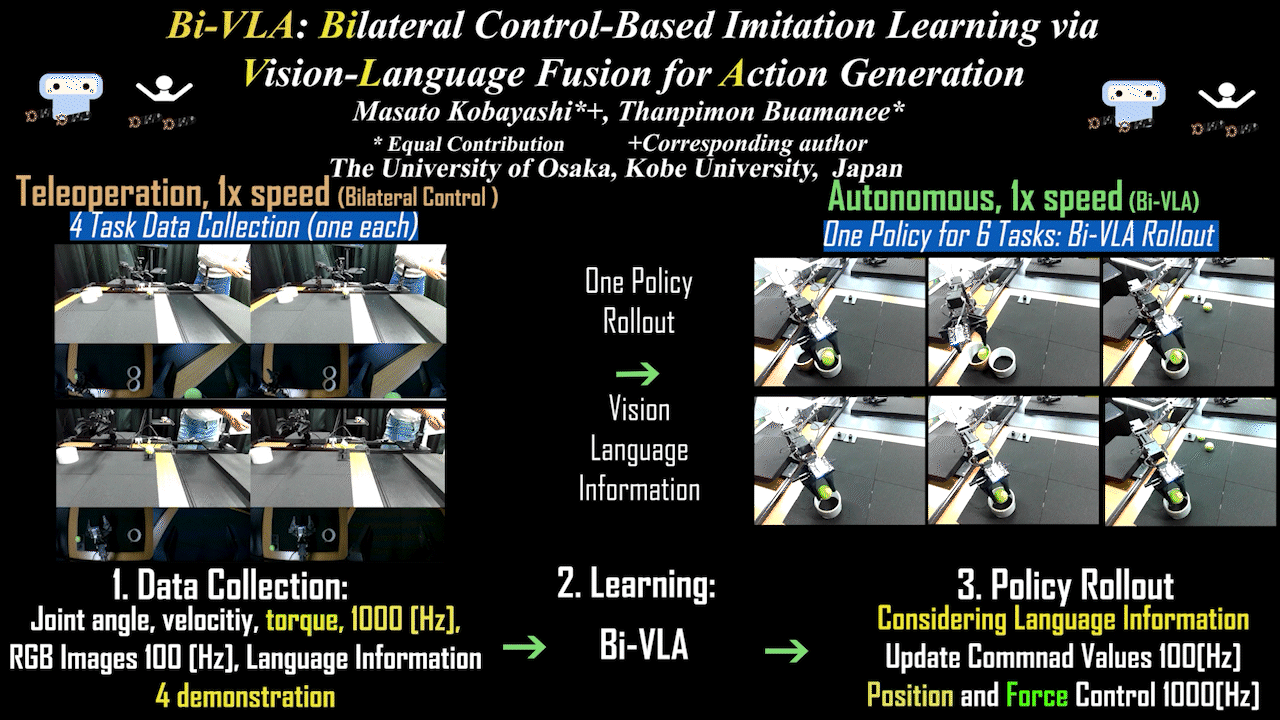
Bi-VLA
Bi-VLA: Bilateral Control-Based Imitation Learning via Vision-Language Fusion for Action Generation
Bilateral control-based imitation learning via language-guided visual information adjustment. Achieves action generation by integrating natural language instructions with visual information.
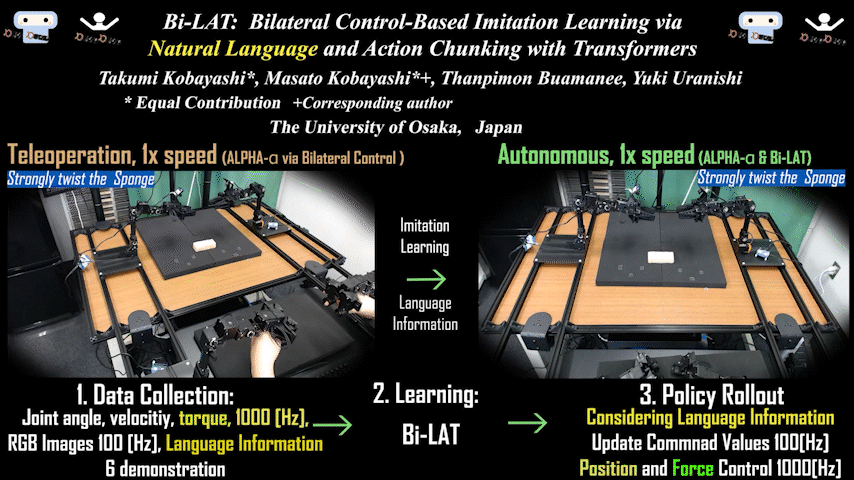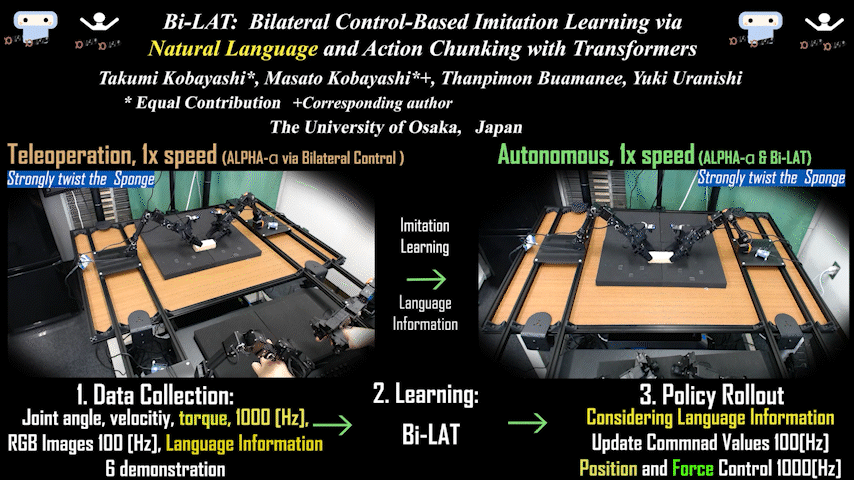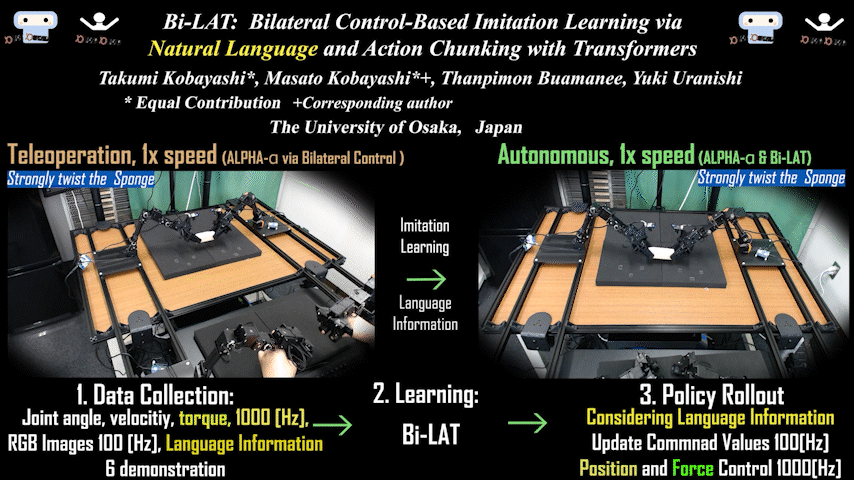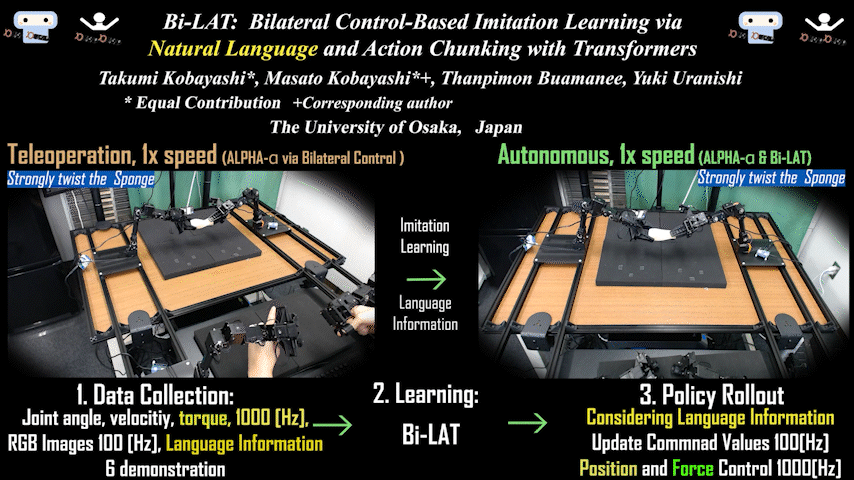
Bi-LAT
Bi-LAT: Bilateral Control-Based Imitation Learning via Natural Language and Action Chunking with Transformers
Bilateral control-based imitation learning combining natural language and action chunking. Achieves flexible robot manipulation with force consideration through language instructions.

ALPHA-α and Bi-ACT
ALPHA-α and Bi-ACT Are All You Need: Importance of Position and Force Control and Information in Imitation Learning for Unimanual and Bimanual Robotic Manipulation
Proposes the importance of position and force control and information in low-cost single-arm and dual-arm robot manipulation for research in daily tasks. Demonstrates the effectiveness of bilateral control-based imitation learning Bi-ACT. Examples include egg transportation and bottle cap opening.
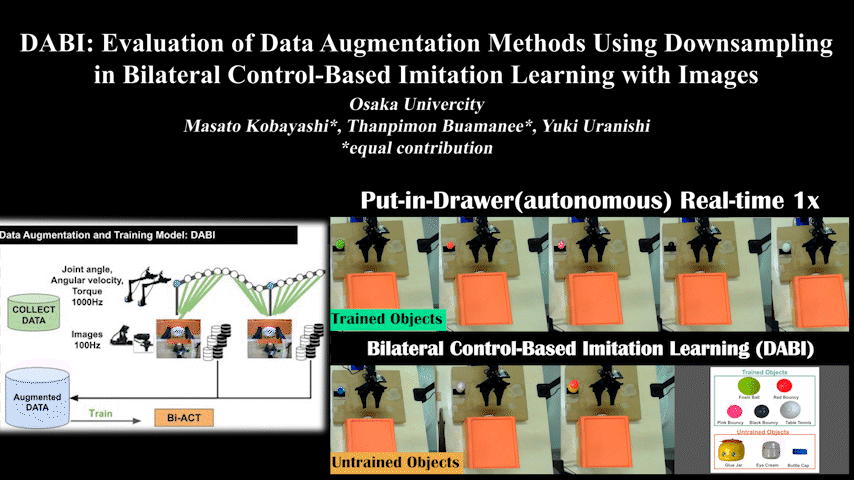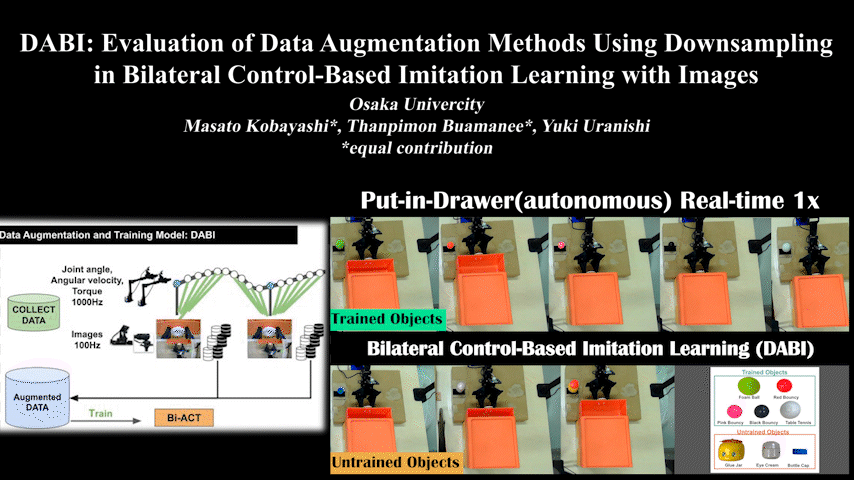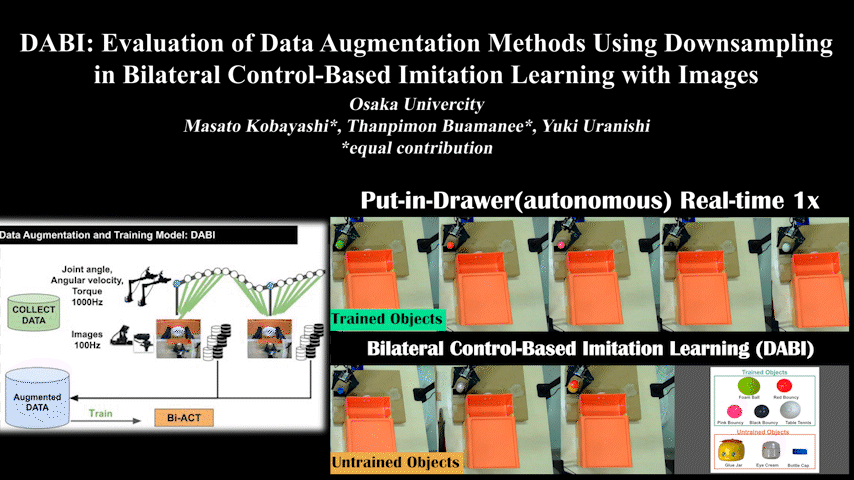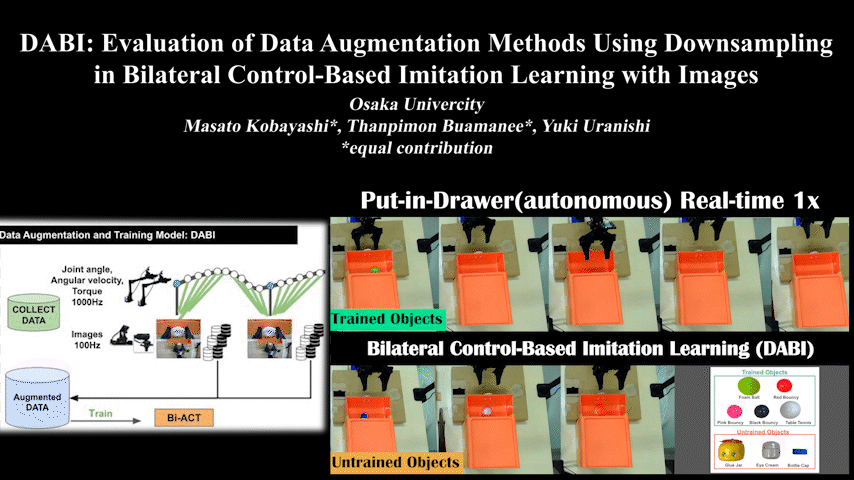
DABI
DABI: Evaluation of Data Augmentation Methods Using Downsampling in Bilateral Control-Based Imitation Learning with Images
Evaluation of data augmentation methods using downsampling in bilateral control-based imitation learning with images. Addresses different sensor frequencies.
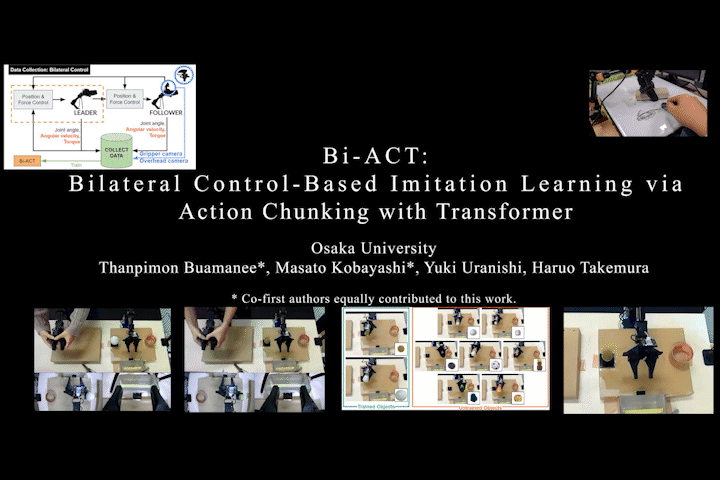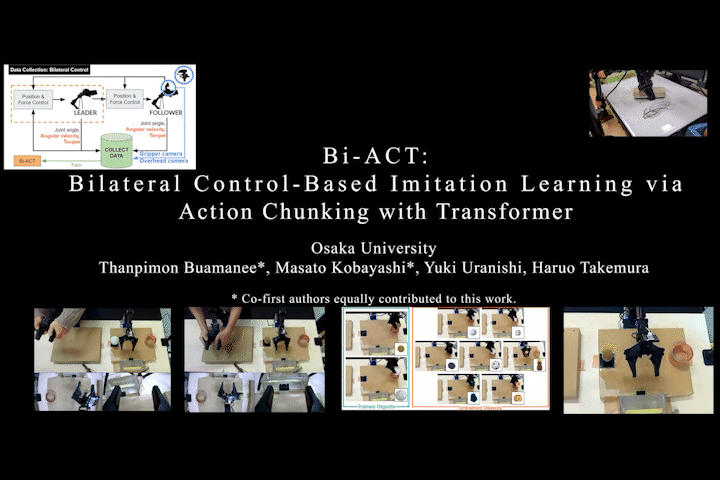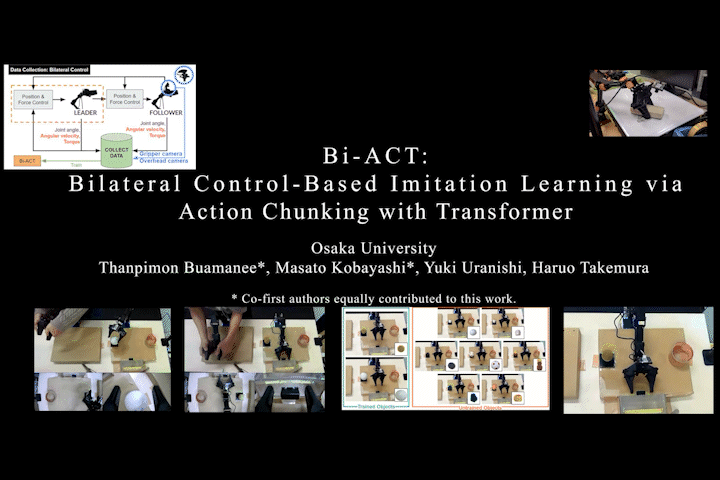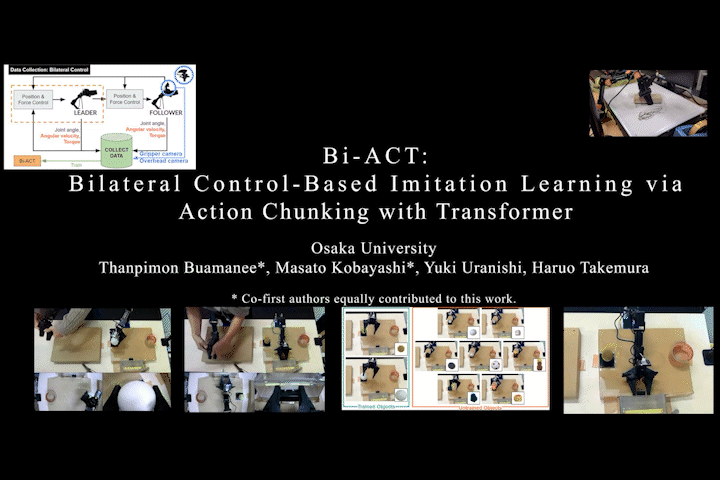
Bi-ACT
Bi-ACT: Bilateral Control-Based Imitation Learning via Action Chunking with Transformer
Proposes Bi-ACT, which fuses the well-known Action Chunking with Transformers (ACT) from ALOHA/ACT with bilateral control-based imitation learning using position and force control. The importance of force control for generalization to unseen objects became clear.
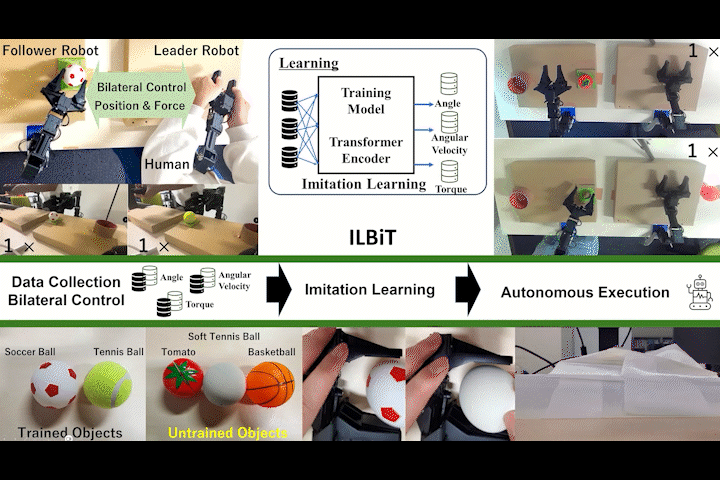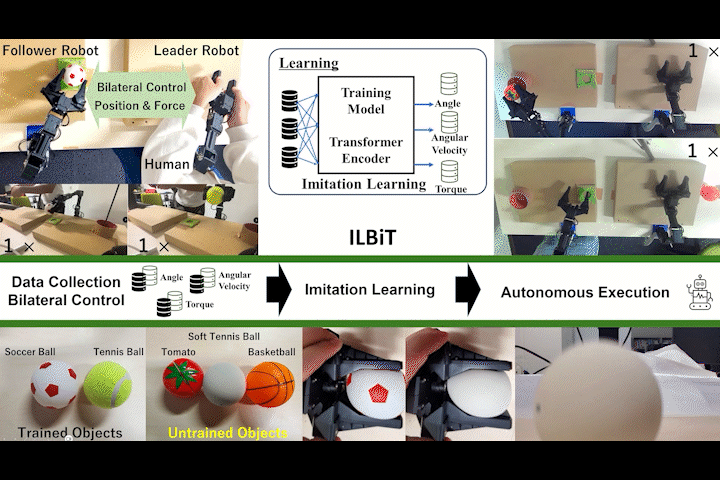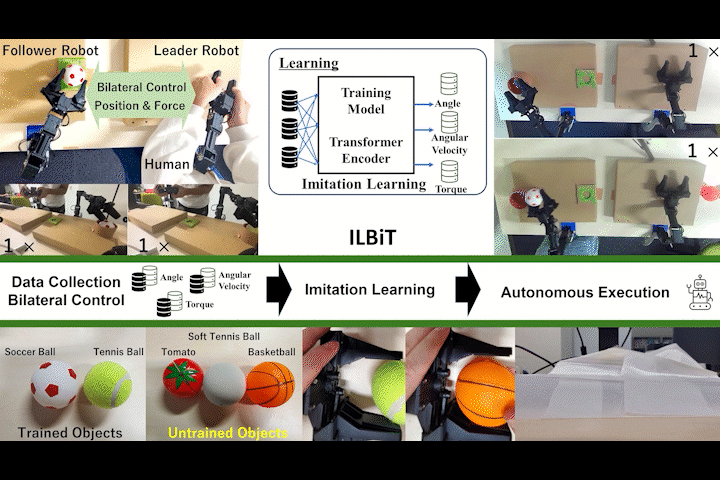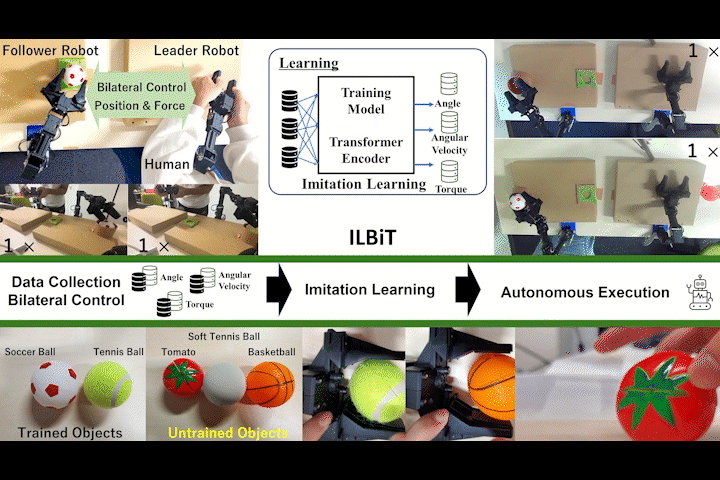
ILBiT
ILBiT: Imitation Learning for Robot Using Position and Torque Information based on Bilateral Control with Transformer
Bilateral control-based imitation learning using position and torque information with Transformer Encoder.
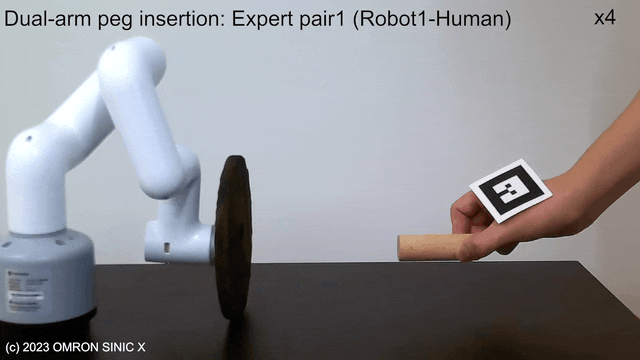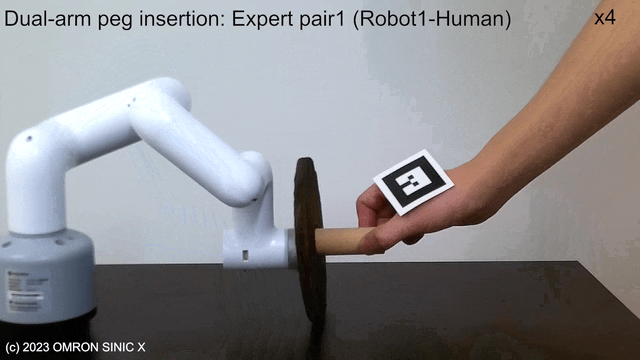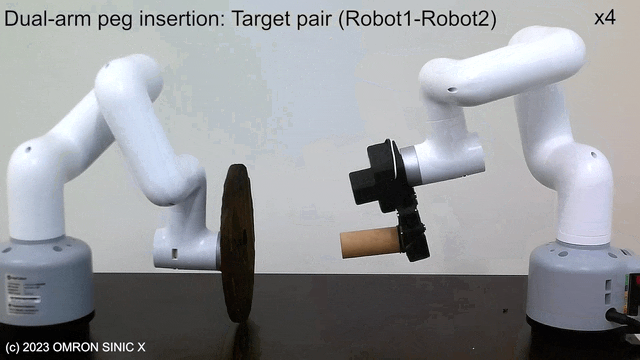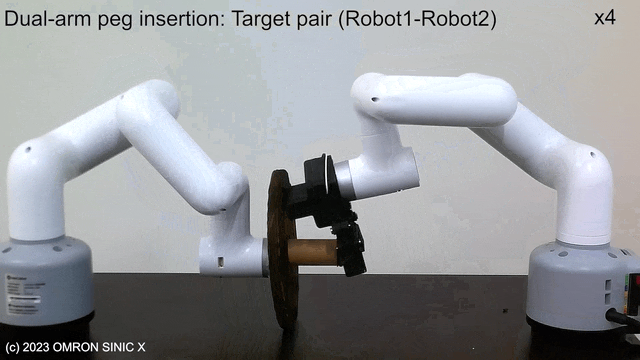
LfDT
LfDT: Learning Dual-Arm Manipulation from Demonstration Translated from a Human and Robotic Arm
Proposes LfDT, a framework for dual-arm coordination tasks that performs domain translation from human-robot demonstration data pairs to robot-robot demonstration data, enabling imitation learning. Cross-domain correspondence in a CycleGAN-like manner.
Mixed Reality-based Robot Interface
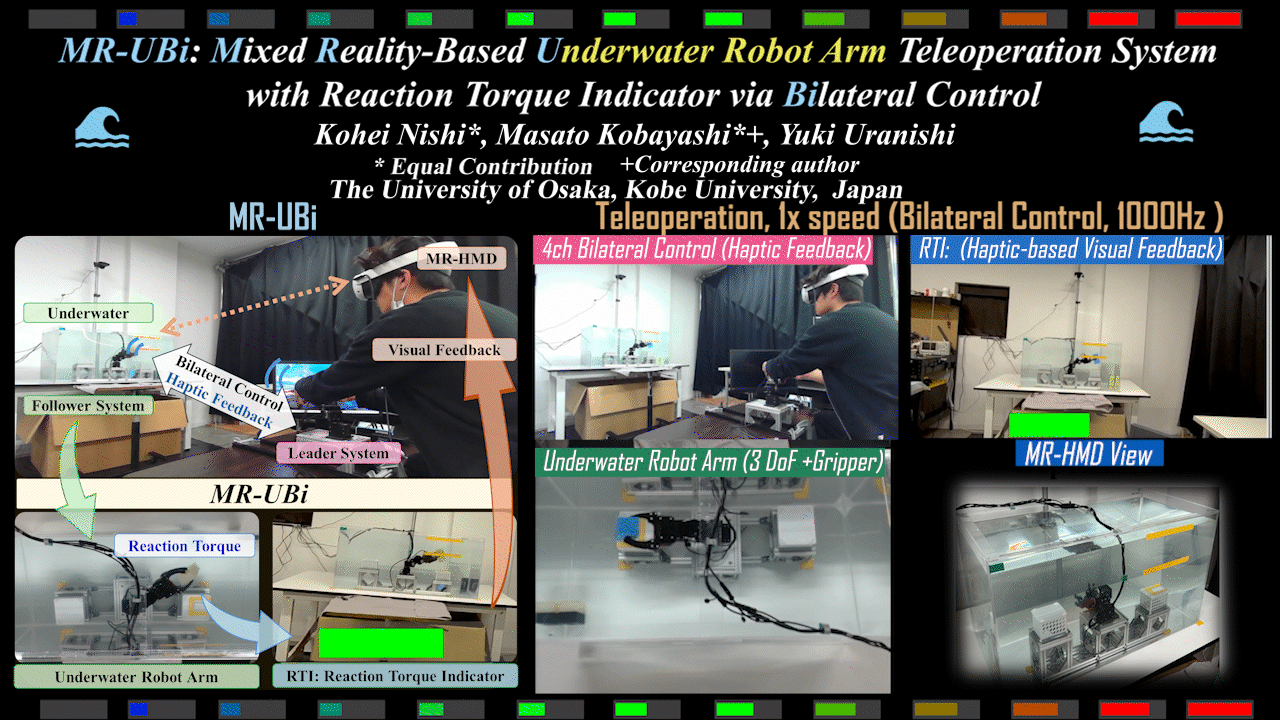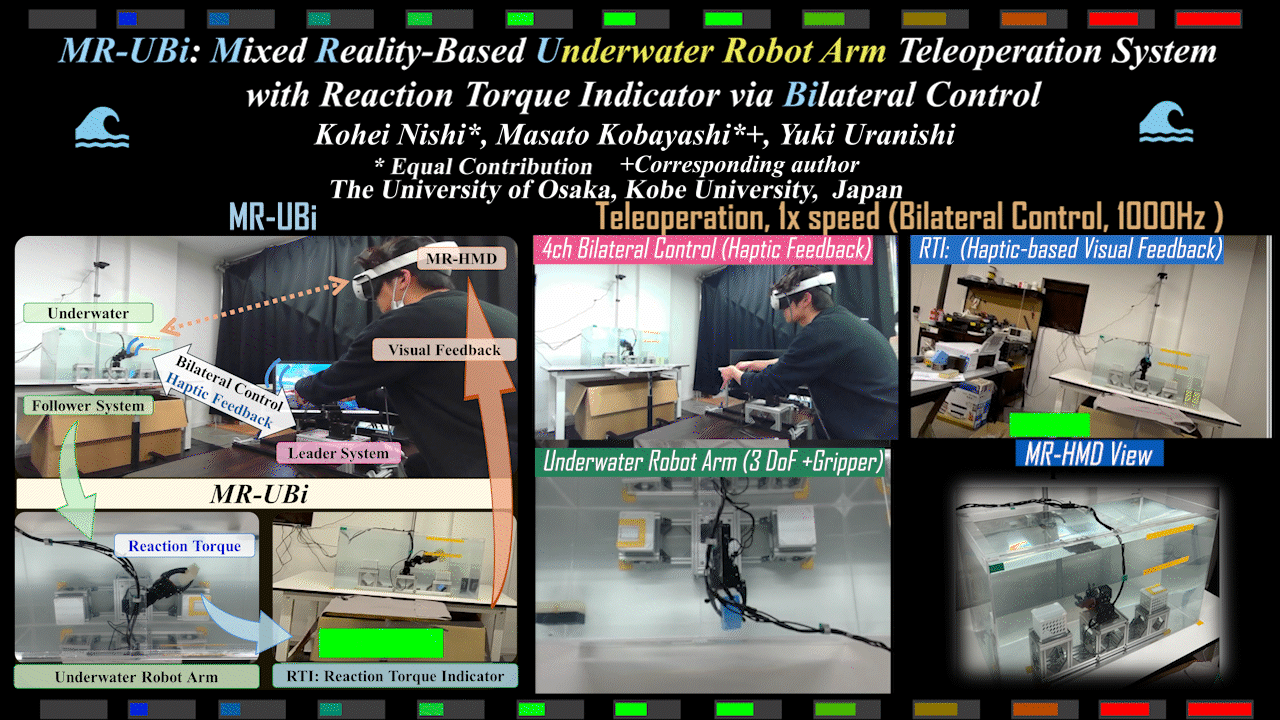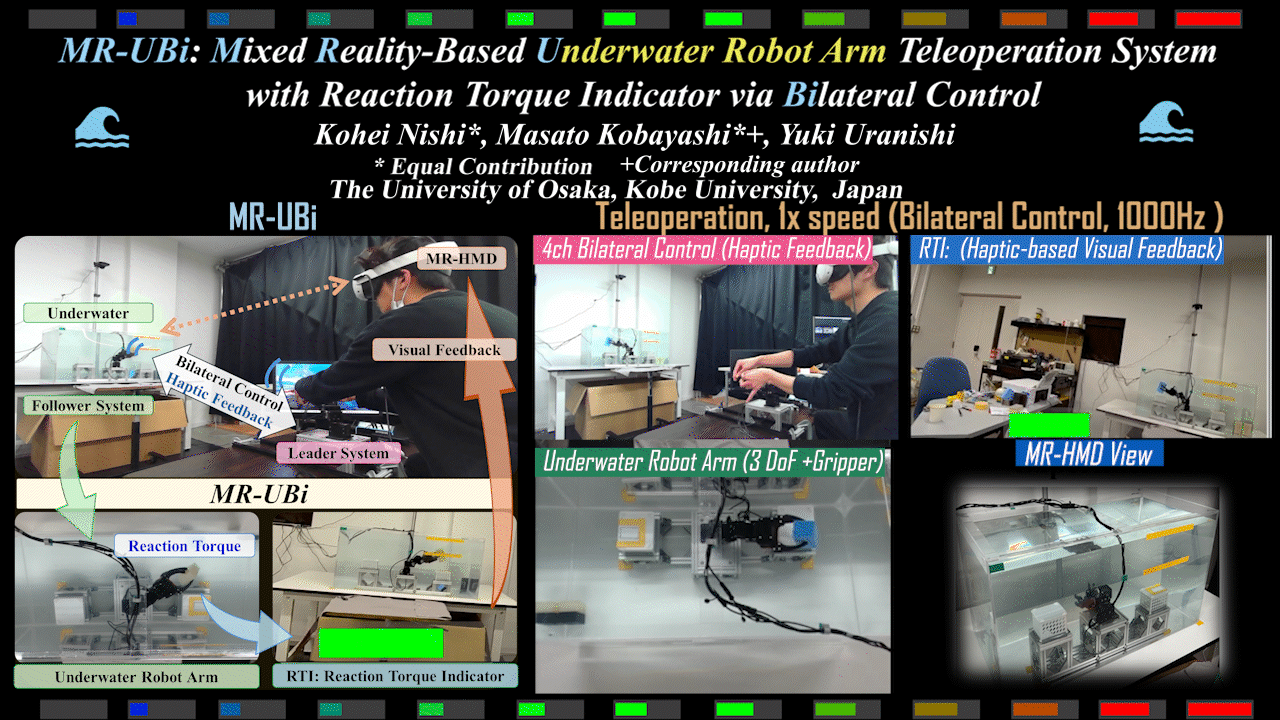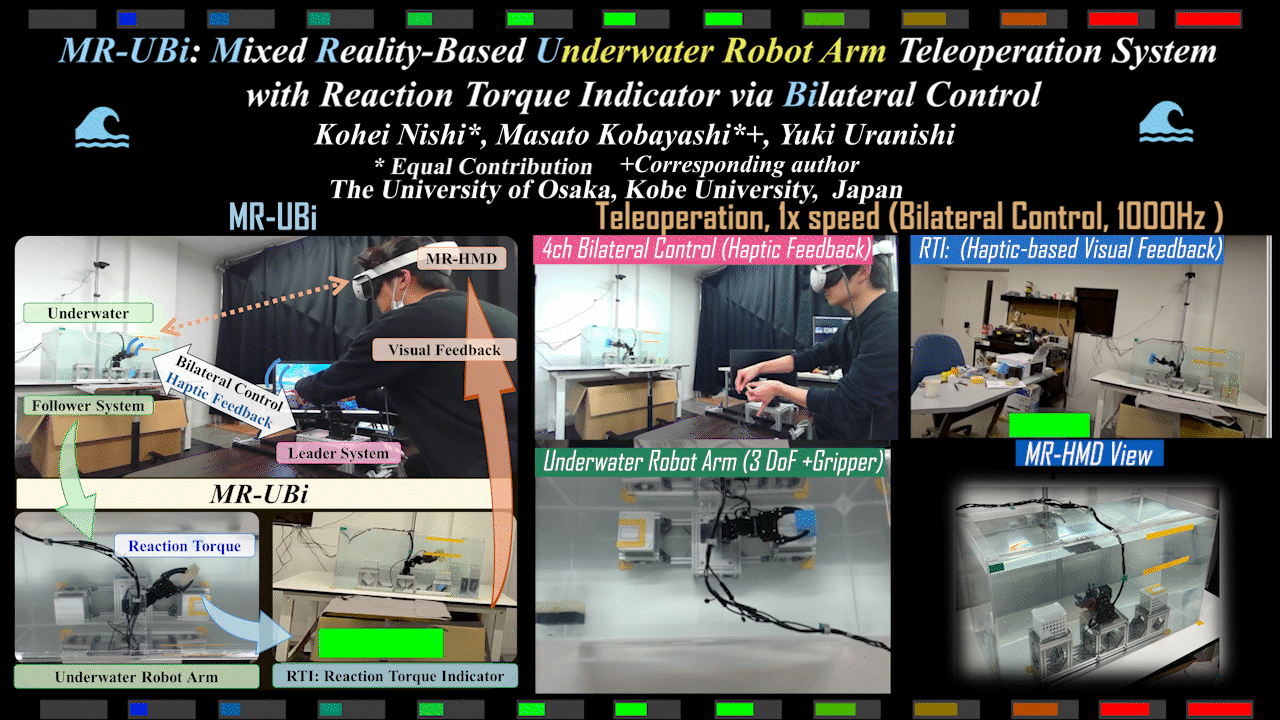
MR-UBi
MR-UBi: Mixed Reality-Based Underwater Robot Arm Teleoperation System with Reaction Torque Indicator via Bilateral Control
Mixed Reality (MR)-based underwater robot arm teleoperation system with reaction torque indicator for underwater environments. Achieves intuitive operation via bilateral control.
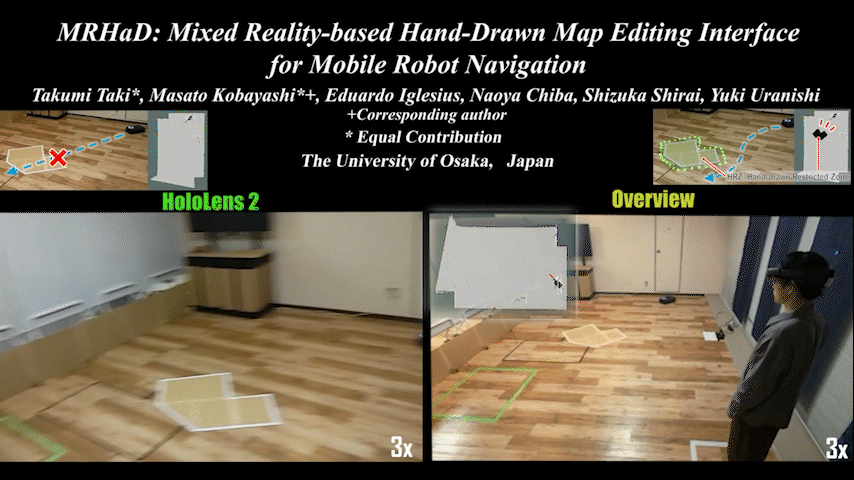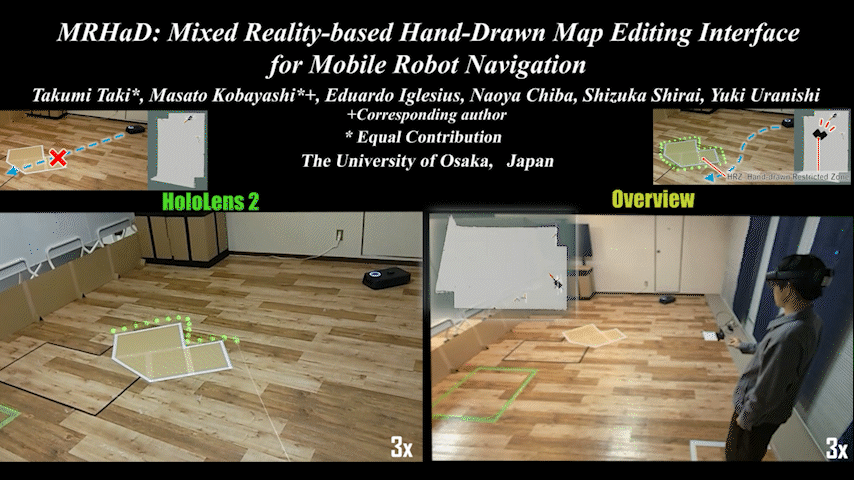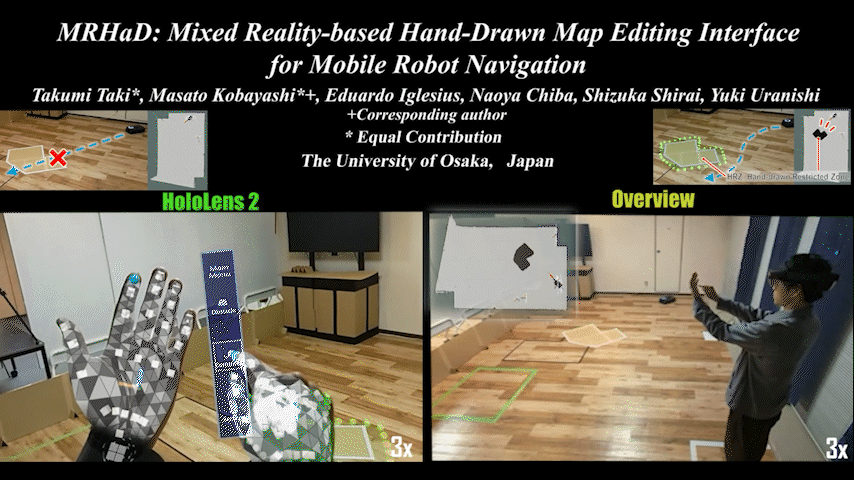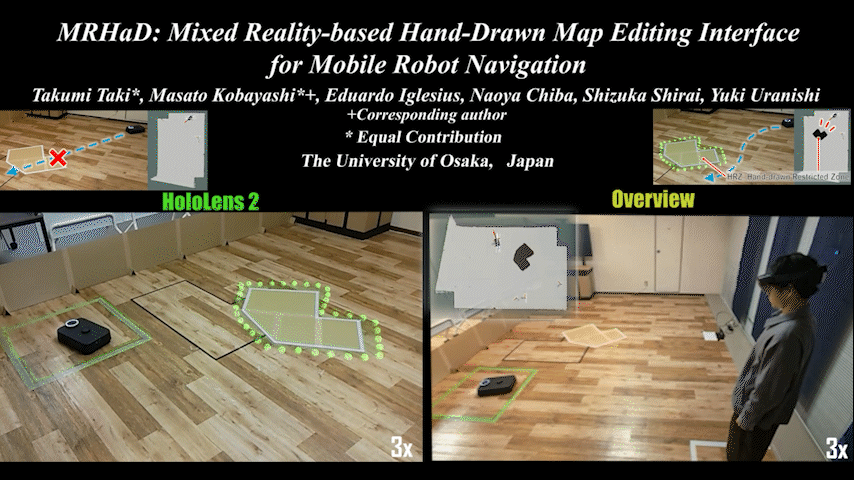
MRHaD
MRHaD: Mixed Reality-based Hand-Drawn Map Editing Interface for Mobile Robot Navigation
Mixed Reality (MR)-based mobile robot navigation system with hand-drawn map editing interface. Achieves intuitive map editing.
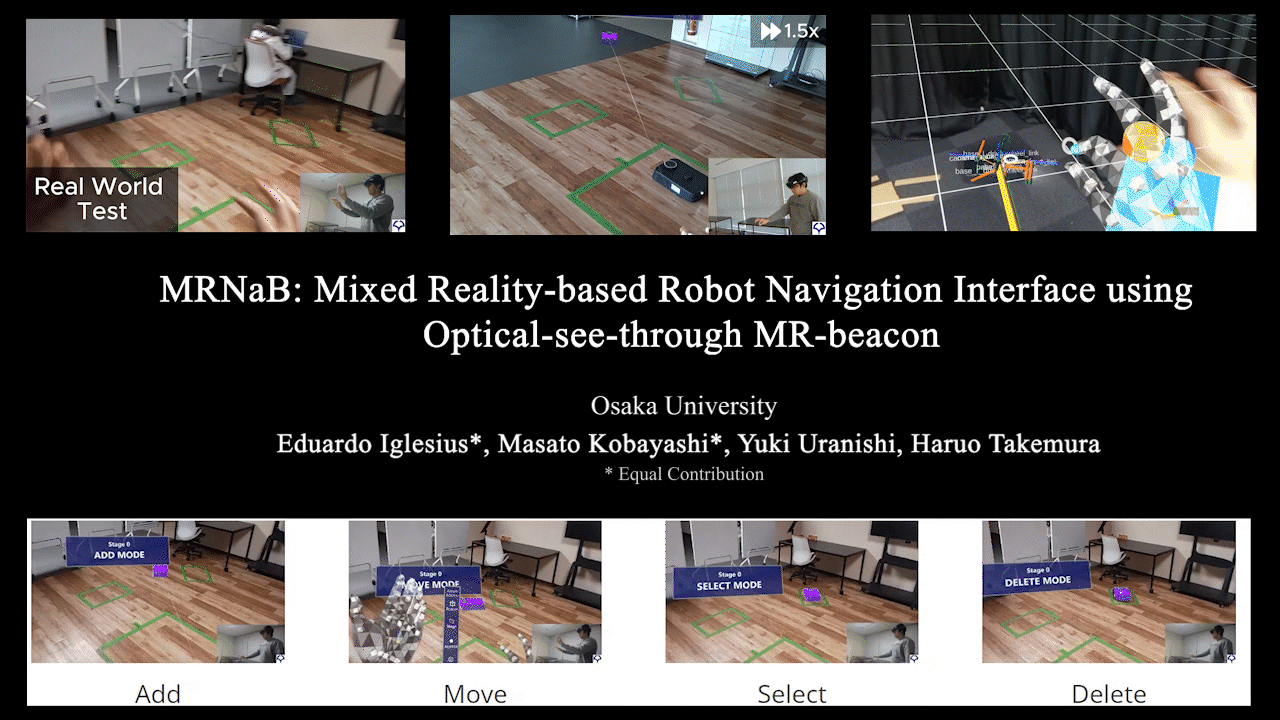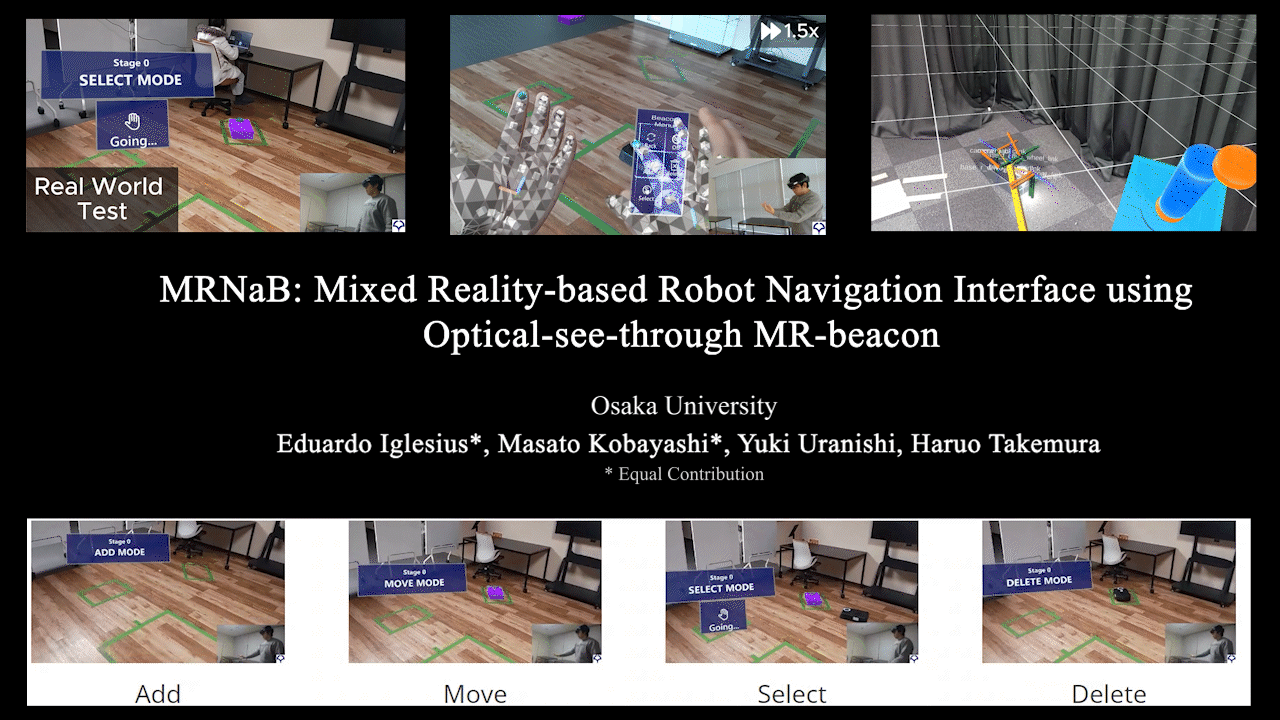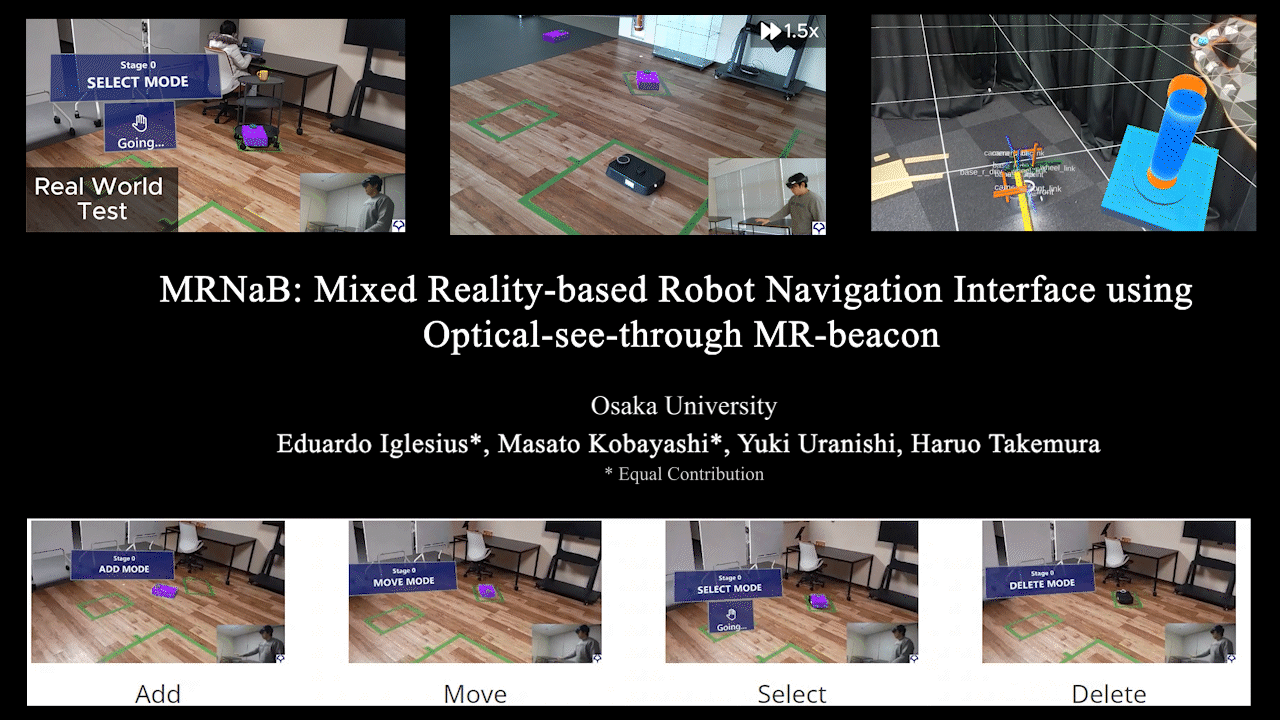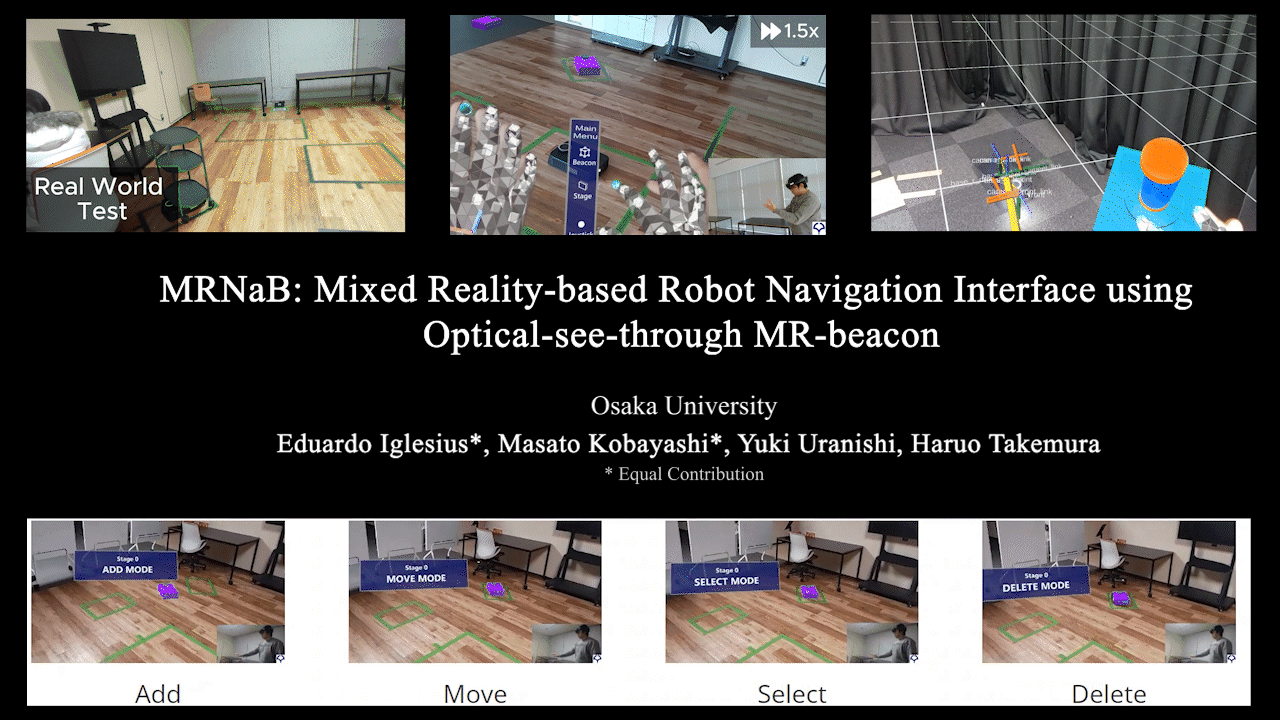
MRNaB
MRNaB: Mixed Reality-based Robot Navigation Interface using Optical-see-through MR-beacon
Mixed Reality (MR)-based robot navigation interface. Achieves navigation through fusion of the real world and virtual space.
Autonomous Mobile Robot
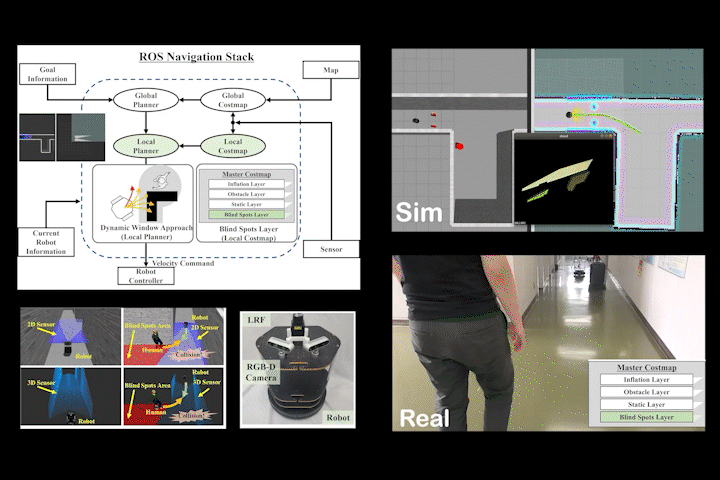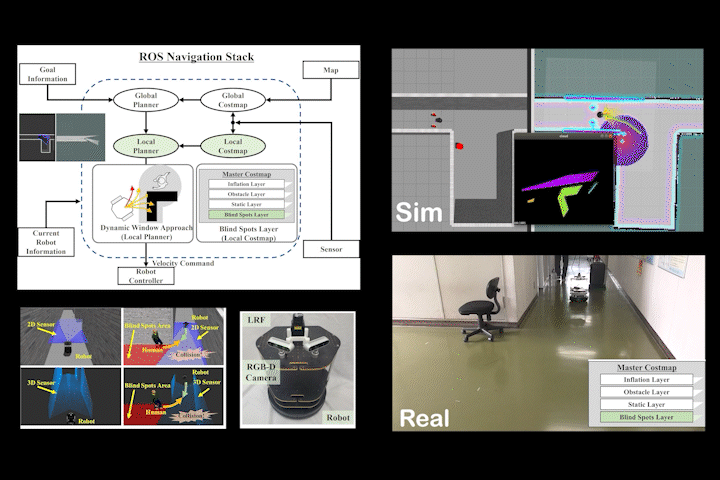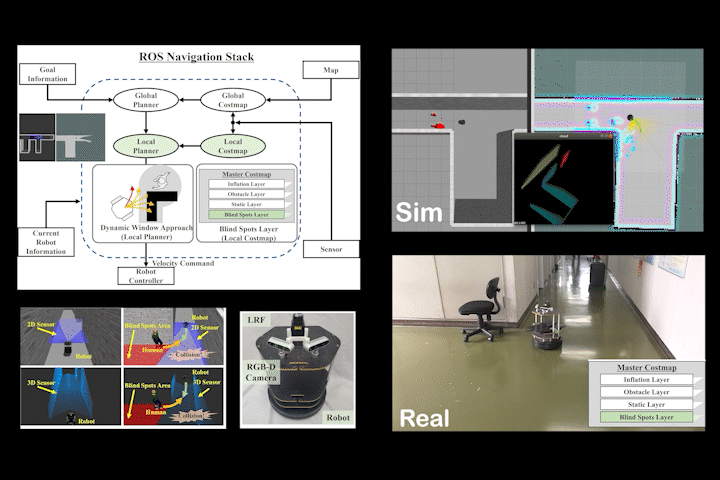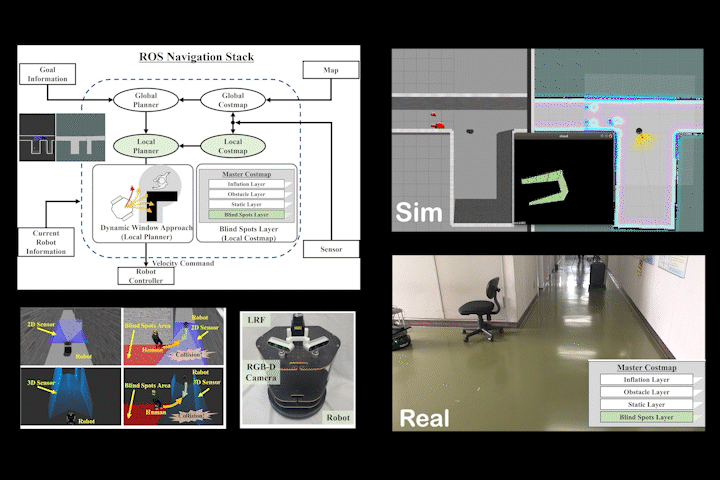
BSL
BSL: Navigation Method Considering Blind Spots Based on ROS Navigation Stack and Blind Spots Layer for Mobile Robot
Navigation method for mobile robots considering sensor blind spots based on ROS Navigation Stack and Blind Spots Layer.
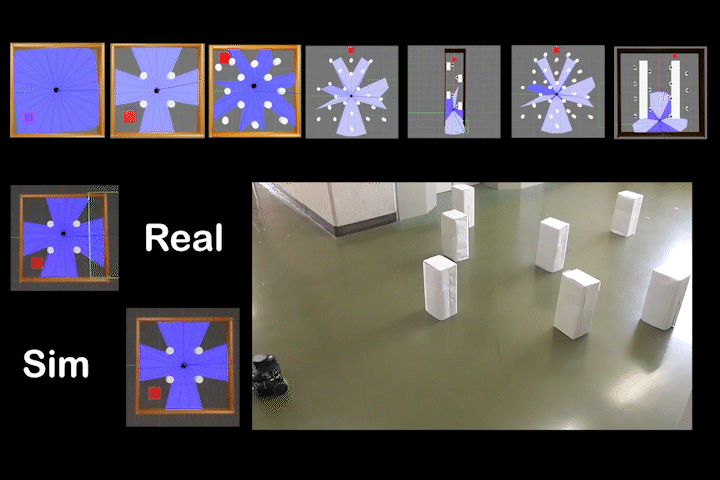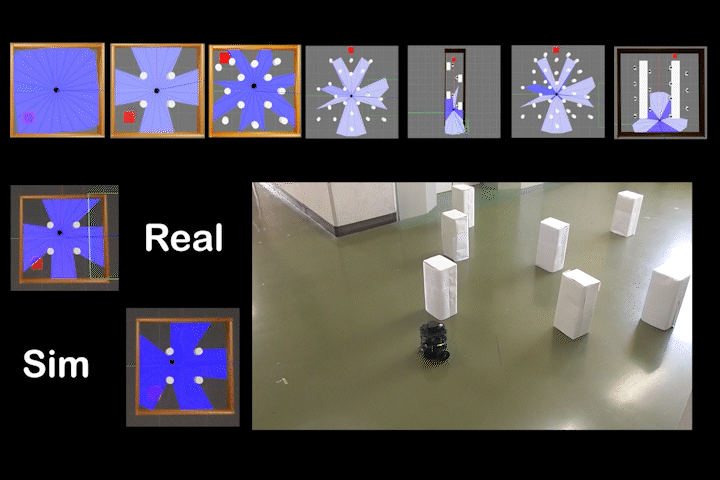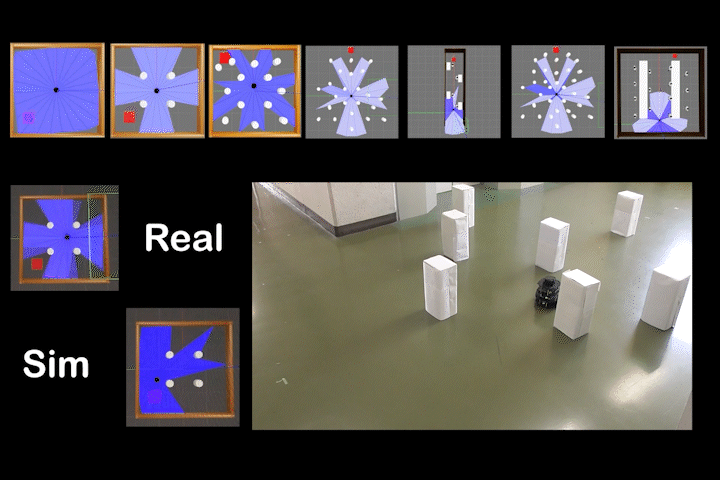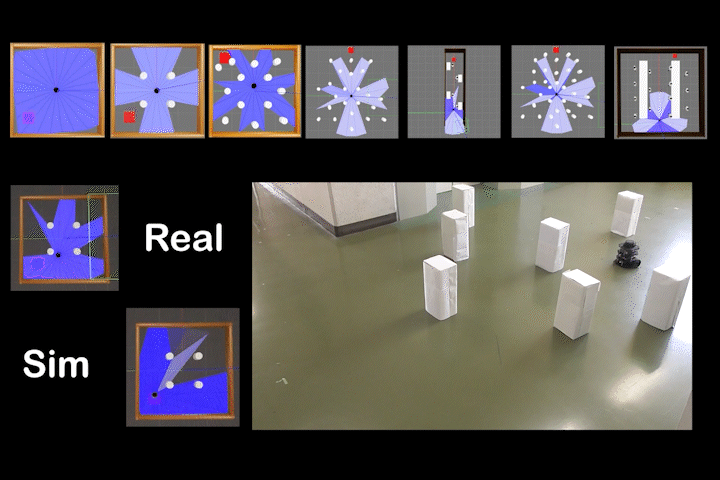
DQDWA
DQDWA: Local Path Planning: Dynamic Window Approach With Q-Learning Considering Congestion Environments for Mobile Robot
Local path planning for mobile robots considering congested environments via dynamic DWA parameter adjustment based on reinforcement learning (Q-Learning).
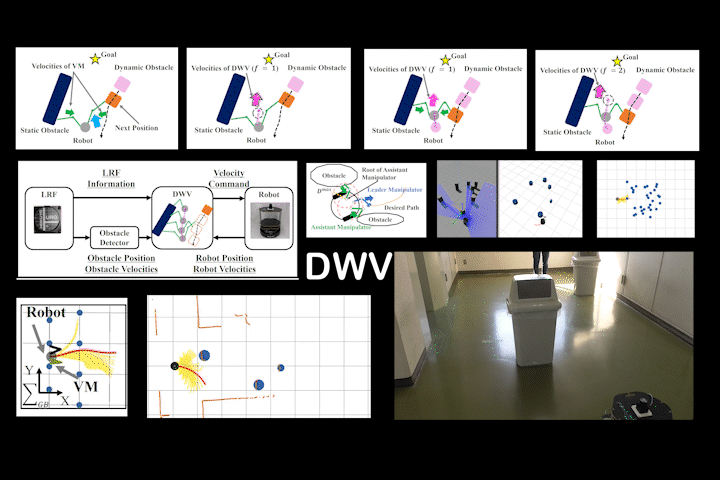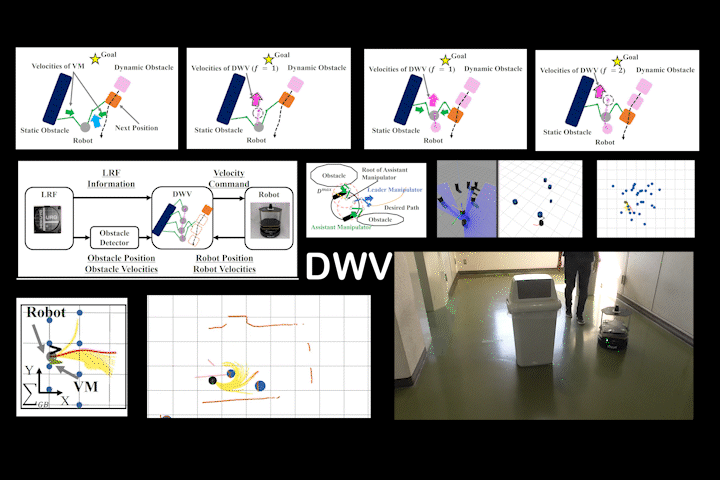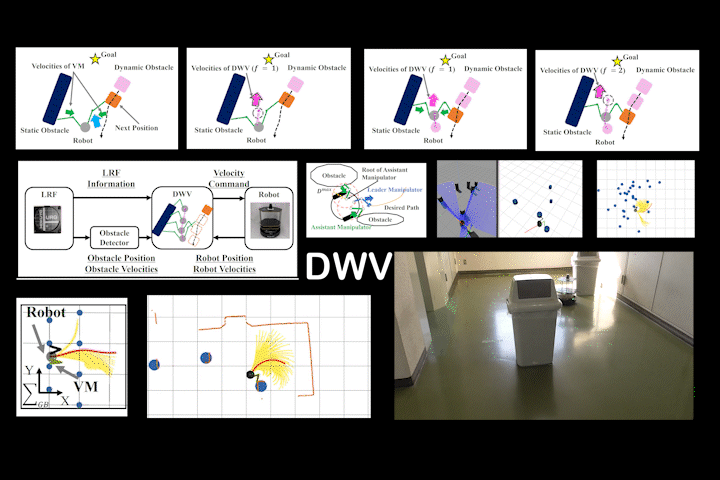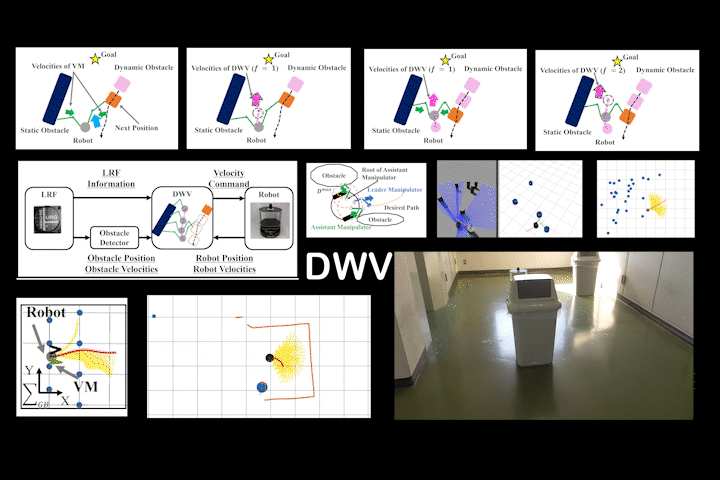
DWV
DWV: Local Path Planning: Dynamic Window Approach With Virtual Manipulators Considering Dynamic Obstacles
Local path planning via DWA with virtual manipulators considering dynamic obstacles. Achieves safe navigation in dynamic environments.
Intelligent Robot System

TRAIL
TRAIL: Team Description Paper for RoboCup@Home 2023
TRAIL team paper for RoboCup@Home 2023. Research on robot manipulation and navigation in home environments.

OUXT Polaris
OUXT Polaris: Autonomous Navigation System for the 2022 Maritime RobotX Challenge
Autonomous navigation system for the Maritime RobotX Challenge. Demonstrates autonomous navigation technology for maritime robots.